Manual MCP server configuration
This page describes manual MCP configuration for Aspire versions 9.0 through 13.0, or for situations where you need more control over the configuration.
The Aspire MCP server is a local Model Context Protocol (MCP) server. Aspire MCP integrates Aspire into your development AI eco-system. With Aspire MCP, you can:
- Query resources, including resource states, endpoints, health status and commands.
- Debug with real-time console logs.
- Investigate development time telemetry, such as structured logs and distributed tracing across resources.
- Execute resource commands.
Get started
Section titled “Get started”There are two ways to configure your AI assistant to use Aspire MCP:
Option 1: Using the Aspire CLI (recommended)
Section titled “Option 1: Using the Aspire CLI (recommended)”The simplest way to get started is using the Aspire CLI, which can automatically detect and configure your AI assistant:
-
Open a terminal in your Aspire project directory.
-
Run the
aspire mcp initcommand:Terminal window aspire mcp init -
Follow the prompts to select which AI assistants to configure.
-
The CLI will automatically set up the MCP server configuration for your selected environments.
For more information, see the aspire mcp command documentation.
Option 2: Manual configuration
Section titled “Option 2: Manual configuration”You can also manually configure your AI assistant to use Aspire MCP:
- Run your Aspire app.
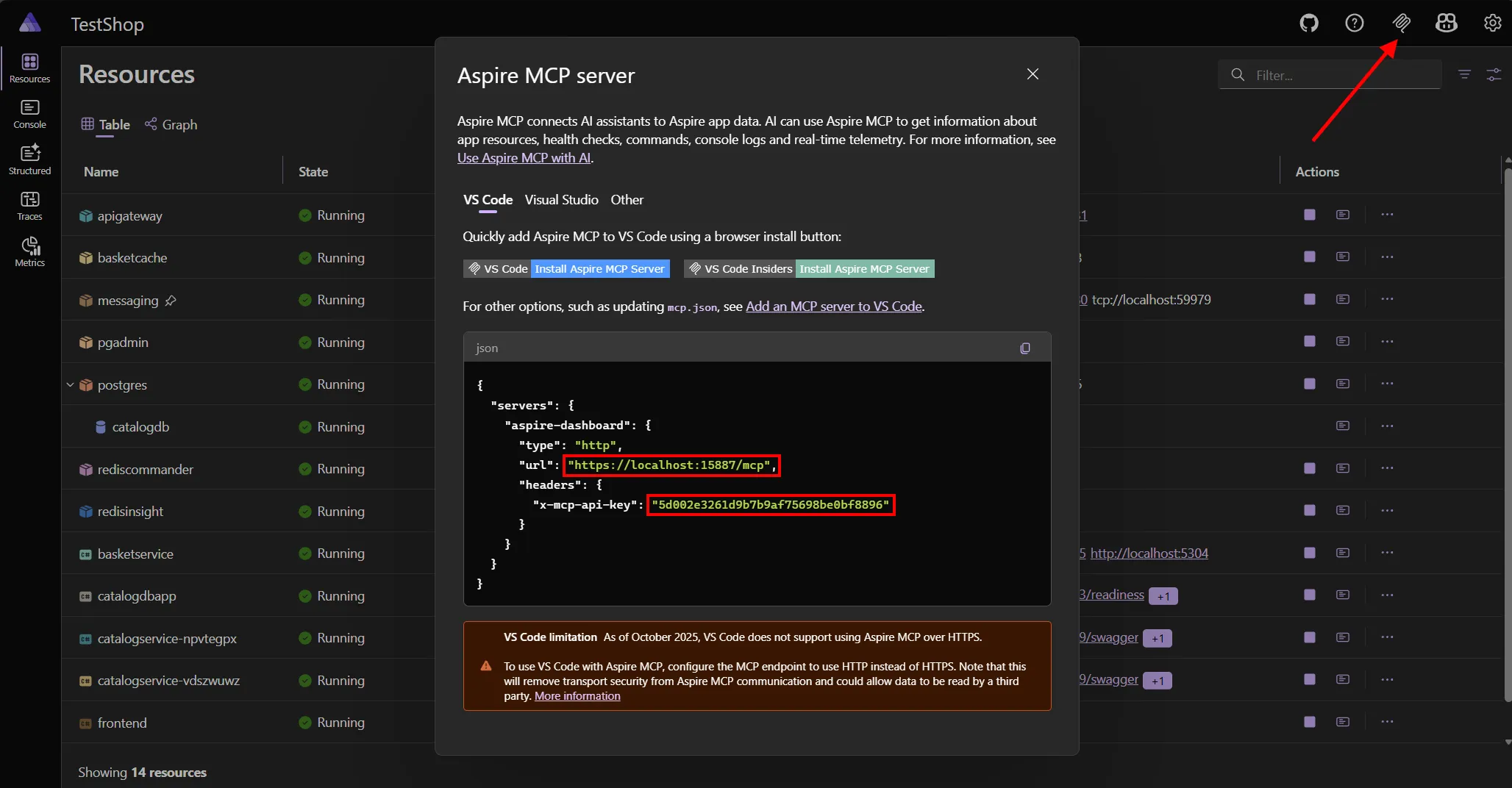
- Open the Aspire dashboard and click on the MCP button in the top right corner of the dashboard. This launches a dialog that contains instructions for using Aspire MCP.
- Use the specified details in the dialog to configure your local AI assistant.
Important settings required to use Aspire MCP:
url- Aspire MCP address.type-httpto indicate Aspire MCP is a streamable-HTTP MCP server.x-mcp-api-key- An HTTP header with a key to secure access to the MCP server.
There isn’t a standard way to configure AI assistants with new MCP servers. Configuration varies depending on your local AI assistant:
The x-mcp-api-key value is used to secure access to the MCP, but the AI assistant must have access to it. Use features in the AI assistant to securely store the value. For example, if you’re using VS Code then input variables can be used to configure the API key and avoid adding the API key to source control in an mcp.json file.
Your first prompts
Section titled “Your first prompts”After configuration, try asking your AI assistant:
“Are all my resources running?”
“Analyze HTTP requests performance for RESOURCE_NAME.”
“Restart unhealthy resources.”
The Aspire MCP server provides the following tools:
Resource management
Section titled “Resource management”list_resources- Lists all resources, including their state, health status, source, endpoints, and commands.execute_resource_command- Executes a resource command. This tool accepts parameters for the resource name and command name.
Logging and telemetry
Section titled “Logging and telemetry”list_console_logs- Lists console logs for a resource.list_structured_logs- Lists structured logs, optionally filtered by resource name.list_traces- Lists distributed traces. Traces can be filtered using an optional resource name parameter.list_trace_structured_logs- Lists structured logs for a trace.
Integration discovery
Section titled “Integration discovery”list_integrations- Lists all available Aspire hosting integrations with their package IDs and versions.get_integration_docs- Retrieves documentation for a specific Aspire hosting integration package.
AppHost management
Section titled “AppHost management”list_apphosts- Lists all available AppHosts in the workspace.select_apphost- Selects a specific AppHost to work with.
By default all resources, console logs and telemetry is accessible by Aspire MCP. Resources and associated telemetry can be excluded from MCP results by annotating the resource in the app host with ExcludeFromMcp().
var builder = DistributedApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
var apiservice = builder.AddProject<Projects.AspireApp_ApiService>("apiservice") .ExcludeFromMcp();
builder.AddProject<Projects.AspireApp_Web>("webfrontend") .WithExternalHttpEndpoints() .WithReference(apiService);
builder.Build().Run();Troubleshooting
Section titled “Troubleshooting”Aspire MCP is designed to work seamlessly with AI assistants, but you may encounter some setup challenges depending on your environment.
MCP connection secured with self-signed HTTPS certificate not supported by some AI assistants
Section titled “MCP connection secured with self-signed HTTPS certificate not supported by some AI assistants”An MCP connection secured with HTTPS is recommended for security. However, some AI assistants currently don’t support calling endpoints secured with a trusted, self-signed certificate. This includes the Aspire MCP, which is secured using a self-signed certificate.
Currently the only work around for using Aspire MCP with these AI assistants is to configure an http MCP endpoint.
- If you already launch your Aspire app with the
httplaunch profile then your app isn’t using HTTPS and you don’t need to do anything. - If you use HTTPS everywhere, you can configure just the MCP endpoint to use
httpby updating launchSettings.json.- Set
ASPIRE_DASHBOARD_MCP_ENDPOINT_URLto anhttpaddress. - Add
ASPIRE_ALLOW_UNSECURED_TRANSPORTset totrue.
- Set
{ "profiles": { "https": { "commandName": "Project", "launchBrowser": true, "dotnetRunMessages": true, "applicationUrl": "https://localhost:15887;http://localhost:15888", "environmentVariables": { "ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT": "Development", "DOTNET_ENVIRONMENT": "Development", "ASPIRE_DASHBOARD_OTLP_ENDPOINT_URL": "https://localhost:16037", "ASPIRE_DASHBOARD_OTLP_HTTP_ENDPOINT_URL": "https://localhost:16038", "ASPIRE_RESOURCE_SERVICE_ENDPOINT_URL": "https://localhost:17037", "ASPIRE_DASHBOARD_MCP_ENDPOINT_URL": "http://localhost:16036", "ASPIRE_ALLOW_UNSECURED_TRANSPORT": "true" } } }}Limitations
Section titled “Limitations”Aspire MCP is a powerful tool, but there are a few things to keep in mind when using it.
Data size
Section titled “Data size”AI models have limits on how much data they can process at once. Aspire MCP may limit the amount of data returned from tools when necessary.
- Large data fields (e.g., long exception stack traces) may be truncated.
- Requests involving large collections of telemetry may be shortened by omitting older items.