Azure Functions integration
Questi contenuti non sono ancora disponibili nella tua lingua.
Azure Functions is a serverless compute service that lets you run event-triggered code without having to explicitly provision or manage infrastructure. The Aspire Azure Functions integration enables you to model Azure Functions projects as part of your distributed application.
It’s expected that you’ve installed the required Azure tooling:
Supported scenarios
Section titled “Supported scenarios”The Aspire Azure Functions integration has several key supported scenarios. This section outlines the scenarios and provides details related to the implementation of each approach.
Supported triggers
Section titled “Supported triggers”The following table lists the supported triggers for Azure Functions in the Aspire integration:
| Trigger | Attribute | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Azure Event Hubs trigger | EventHubTrigger | 📦 Aspire.Hosting.Azure.EventHubs |
| Azure Service Bus trigger | ServiceBusTrigger | 📦 Aspire.Hosting.Azure.ServiceBus |
| Azure Storage Blobs trigger | BlobTrigger | 📦 Aspire.Hosting.Azure.Storage |
| Azure Storage Queues trigger | QueueTrigger | 📦 Aspire.Hosting.Azure.Storage |
| Azure CosmosDB trigger | CosmosDbTrigger | 📦 Aspire.Hosting.Azure.CosmosDB |
| HTTP trigger | HttpTrigger | Supported without any additional resource dependencies. |
| Timer trigger | TimerTrigger | Supported without any additional resource dependencies—relies on implicit host storage. |
Deployment
Section titled “Deployment”Deployment to Azure Container Apps (ACA) is supported using the SDK container publish function in Microsoft.Azure.Functions.Worker.Sdk. When deploying to Azure Container Apps, KEDA-based auto-scaling rules will automatically be configured for your functions.
For more information about the Azure Functions integration with Aspire, see Azure Functions and Aspire integration.
Configure external HTTP endpoints
Section titled “Configure external HTTP endpoints”To make HTTP triggers publicly accessible, call the WithExternalHttpEndpoints API on the AzureFunctionsProjectResource. For more information, see Add Azure Functions resource.
Azure Function project constraints
Section titled “Azure Function project constraints”The Aspire Azure Functions integration has the following project constraints:
- You must target .NET 8.0 or later.
- You must use a .NET 9 SDK or later.
- It currently only supports .NET workers with the isolated worker model.
- Requires the following NuGet packages:
- 📦 Microsoft.Azure.Functions.Worker: Use the
FunctionsApplicationBuilder. - 📦 Microsoft.Azure.Functions.Worker.Sdk: Adds support for
aspire runandaspire deploy. - 📦 Microsoft.Azure.Functions.Http.AspNetCore: Adds HTTP trigger-supporting APIs.
- 📦 Microsoft.Azure.Functions.Worker: Use the
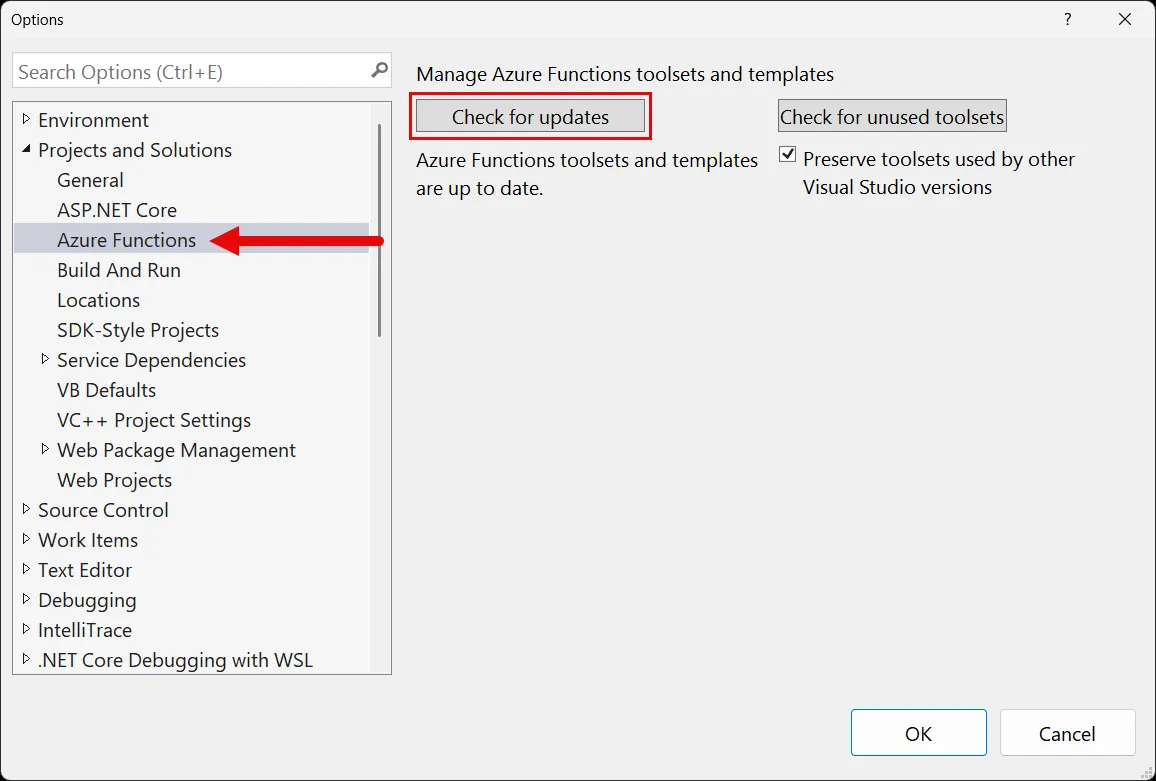
If you encounter issues with the Azure Functions project, such as:
There is no Functions runtime available that matches the version specified in the project
In Visual Studio, try checking for an update on the Azure Functions tooling. Open the Options dialog, navigate to Projects and Solutions, and then select Azure Functions. Select the Check for updates button to ensure you have the latest version of the Azure Functions tooling:
Hosting integration
Section titled “Hosting integration”The Aspire Azure Functions hosting integration models Azure Functions projects as the AzureFunctionsProjectResource type. To access this type and APIs for expressing them within your AppHost project, install the 📦 Aspire.Hosting.Azure.Functions NuGet package:
aspire add azure-functionsLa CLI Aspire è interattiva; seleziona il risultato corretto quando richiesto:
Select an integration to add:
> azure-functions (Aspire.Hosting.Azure.Functions)> Other results listed as selectable options...#:package Aspire.Hosting.Azure.Functions@*<PackageReference Include="Aspire.Hosting.Azure.Functions" Version="*" />Add Azure Functions resource
Section titled “Add Azure Functions resource”In your AppHost project, call AddAzureFunctionsProject on the builder instance to add an Azure Functions resource. There are two ways to add an Azure Functions project, depending on whether the Functions project is referenced in your AppHost project.
Add a referenced Functions project
Section titled “Add a referenced Functions project”If the Azure Functions project is referenced in your AppHost project, use the generic overload of AddAzureFunctionsProject:
var builder = DistributedApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
var functions = builder.AddAzureFunctionsProject<Projects.ExampleFunctions>("functions") .WithExternalHttpEndpoints();
builder.AddProject<Projects.ExampleProject>() .WithReference(functions) .WaitFor(functions);
// After adding all resources, run the app...Add a Functions project by file path
Section titled “Add a Functions project by file path”If the Azure Functions project is not referenced in your AppHost project, you can add it by specifying the path to the project file:
var builder = DistributedApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
var functions = builder.AddAzureFunctionsProject("functions", "../MyFunctions/MyFunctions.csproj") .WithExternalHttpEndpoints();
builder.AddProject<Projects.ExampleProject>() .WithReference(functions) .WaitFor(functions);
// After adding all resources, run the app...In the preceding example, the path to the Functions project file is relative to the AppHost project directory. If the path is not absolute, it will be resolved relative to the AppHost directory.
When Aspire adds an Azure Functions project resource to the AppHost, as shown in the preceding examples, the functions resource can be referenced by other project resources. The WithReference method configures a connection in the ExampleProject named "functions". If the Azure Resource was deployed and it exposed an HTTP trigger, its endpoint would be external due to the call to WithExternalHttpEndpoints.
Add Azure Functions resource with host storage
Section titled “Add Azure Functions resource with host storage”If you want to modify the default host storage account that the Azure Functions host uses, call the WithHostStorage method on the Azure Functions project resource:
var builder = DistributedApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
var storage = builder.AddAzureStorage("storage") .RunAsEmulator();
var functions = builder.AddAzureFunctionsProject<Projects.ExampleFunctions>("functions") .WithHostStorage(storage);
builder.AddProject<Projects.ExampleProject>() .WithReference(functions) .WaitFor(functions);
// After adding all resources, run the app...The preceding code relies on the 📦 Aspire.Hosting.Azure.Storage NuGet package to add an Azure Storage resource that runs as an emulator. The storage resource is then passed to the WithHostStorage API, explicitly setting the host storage to the emulated resource.
Reference resources in Azure Functions
Section titled “Reference resources in Azure Functions”To reference other Azure resources in an Azure Functions project, chain a call to WithReference on the Azure Functions project resource and provide the resource to reference:
var builder = DistributedApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
var storage = builder.AddAzureStorage("storage").RunAsEmulator();var blobs = storage.AddBlobs("blobs");
builder.AddAzureFunctionsProject<Projects.ExampleFunctions>("functions") .WithHostStorage(storage) .WithReference(blobs);
builder.Build().Run();The preceding code adds an Azure Storage resource to the AppHost and references it in the Azure Functions project. The blobs resource is added to the storage resource and then referenced by the functions resource. The connection information required to connect to the blobs resource is automatically injected into the Azure Functions project and enables the project to define a BlobTrigger that relies on blobs resource.