Aspire and GitHub Codespaces
Bu içerik henüz dilinizde mevcut değil.
GitHub Codespaces offers a cloud-hosted development environment based on Visual Studio Code. It can be accessed directly from a web browser or through Visual Studio Code locally, where Visual Studio Code acts as a client connecting to a cloud-hosted backend. With Aspire 9.1, comes logic to better support GitHub Codespaces including:
- Automatically configure port forwarding with the correct protocol.
- Automatically translate URLs in the Aspire dashboard.
Before Aspire 9.1 it was still possible to use Aspire within a GitHub Codespace, however more manual configuration was required.
GitHub Codespaces vs. Dev Containers
Section titled “GitHub Codespaces vs. Dev Containers”GitHub Codespaces builds upon Visual Studio Code and the Dev Containers specification. In addition to supporting GitHub Codespaces, Aspire 9.1 enhances support for using Visual Studio Code and locally hosted Dev Containers. While the experiences are similar, there are some differences. For more information, see Aspire and Visual Studio Code Dev Containers.
Quick start using template repository
Section titled “Quick start using template repository”To configure GitHub Codespaces for Aspire, use the .devcontainer/devcontainer.json file in your repository. The simplest way to get started is by creating a new repository from our template repository. Consider the following steps:
-
Create a new repository using our template.
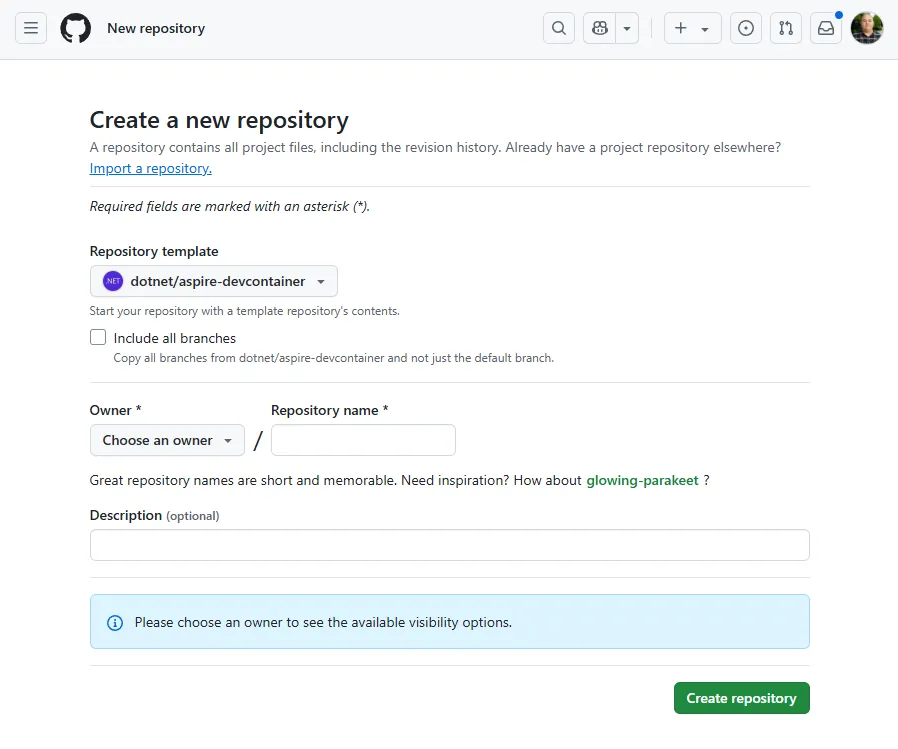
Once you provide the details and select Create repository, the repository is created and shown in GitHub.
-
From the new repository, select on the Code button and select the Codespaces tab and then select Create codespace on main.
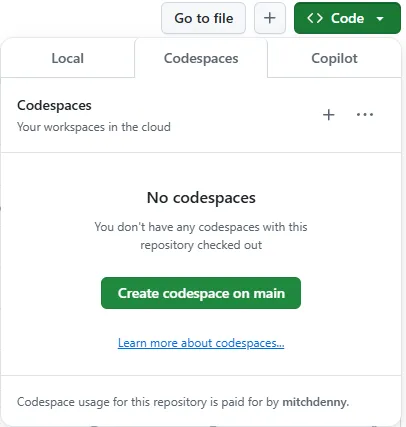
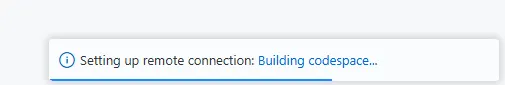
After you select Create codespace on main, you navigate to a web-based version of Visual Studio Code. Before you use the Codespace, the containerized development environment needs to be prepared. This process happens automatically on the server and you can review progress by selecting the Building codespace link on the notification in the bottom right of the browser window.
When the container image has finished being built the Terminal prompt appears which signals that the environment is ready to be interacted with.
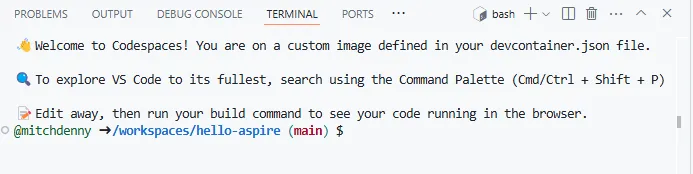
At this point, the Aspire templates have been installed and the ASP.NET Core developer certificate has been added and accepted.
-
Create a new Aspire project using the starter template.
Terminal window dotnet new aspire-starter --name HelloAspireThis results in many files and folders being created in the repository, which are visible in the Explorer panel on the left side of the window.
-
Launch the AppHost via the
HelloAspire.AppHost/AppHost.csfile, by selecting the Run project button near the top-right corner of the Tab bar.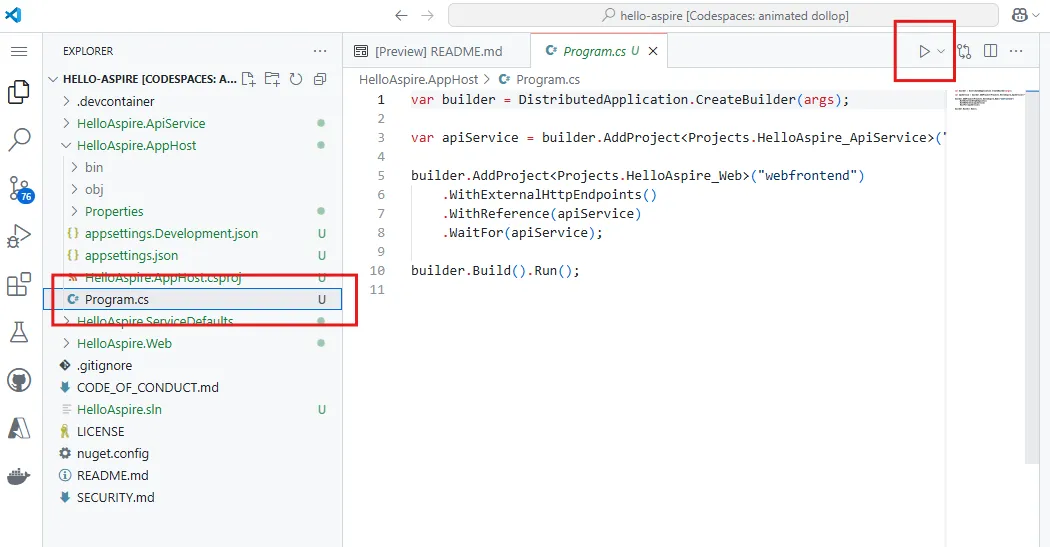
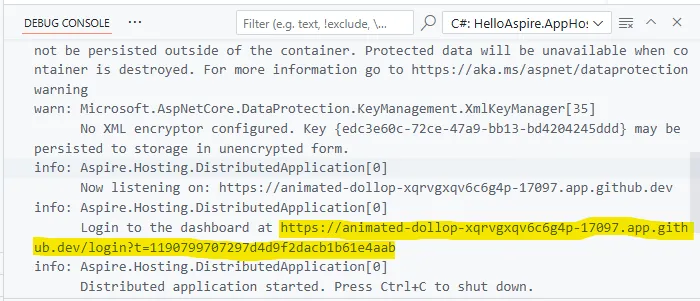
After a few moments the Debug Console panel is displayed, and it includes a link to the Aspire dashboard exposed on a GitHub Codespaces endpoint with the authentication token.
-
Open the Aspire dashboard by selecting the dashboard URL in the Debug Console. This opens the Aspire dashboard in a separate tab within your browser.
You notice on the dashboard that all HTTP/HTTPS endpoints defined on resources have had their typical
localhostaddress translated to a unique fully qualified subdomain on theapp.github.devdomain.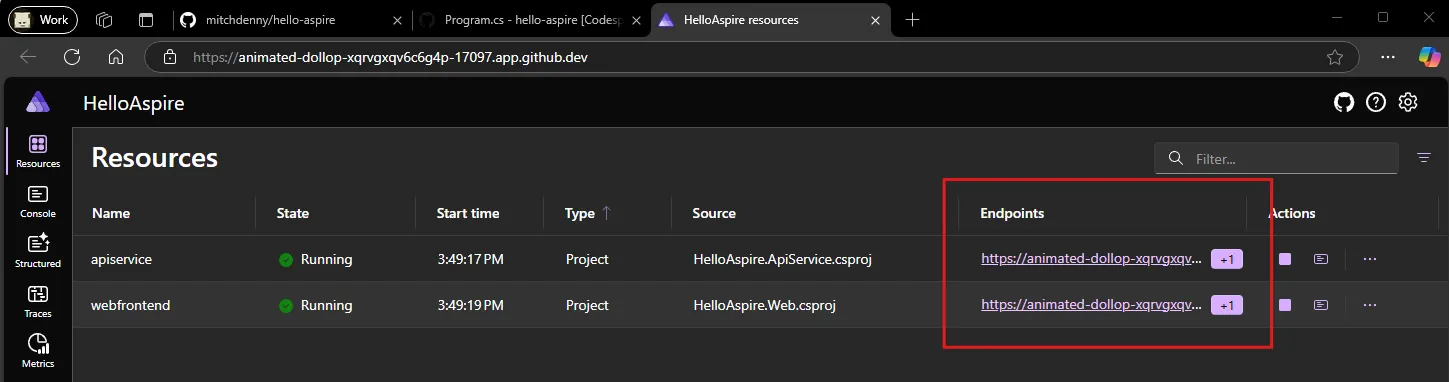
Traffic to each of these endpoints is automatically forwarded to the underlying process or container running within the Codespace. This includes development time tools such as PgAdmin and Redis Insight.
-
Commit changes to the GitHub repository.
GitHub Codespaces doesn’t automatically commit your changes to the branch you’re working on in GitHub. You have to use the Source Control panel to stage and commit the changes and push them back to the repository.
Working in a GitHub Codespace is similar to working with Visual Studio Code on your own machine. You can checkout different branches and push changes just like you normally would. In addition, you can easily spin up multiple Codespaces simultaneously if you want to quickly work on another branch without disrupting your existing debug session. For more information, see Developing in a codespace.
-
Clean up your Codespace.
GitHub Codespaces are temporary development environments and while you might use one for an extended period of time, they should be considered a disposable resource that you recreate as needed (with all of the customization/setup contained within the
devcontainer.jsonand associated configuration files).To delete your GitHub Codespace, visit the GitHub Codespaces page. This shows you a list of all of your Codespaces. From here you can perform management operations on each Codespace, including deleting them.
GitHub charges for the use of Codespaces. For more information, see Managing the cost of GitHub Codespaces in your organization.
Manually configuring devcontainer.json
Section titled “Manually configuring devcontainer.json”The preceding walkthrough demonstrates the streamlined process of creating a GitHub Codespace using the Aspire Devcontainer template. If you already have an existing repository and wish to utilize Devcontainer functionality with Aspire, add a devcontainer.json file to the .devcontainer folder within your repository:
Dizin.devcontainer
- devcontainer.json
The template repository contains a copy of the devcontainer.json file that you can use as a starting point, which should be sufficient for Aspire.
Speed up Codespace creation
Section titled “Speed up Codespace creation”Creating a GitHub Codespace can take some time as it prepares the underlying container image. To expedite this process, you can utilize prebuilds to significantly reduce the creation time to approximately 30-60 seconds (exact timing might vary). For more information on GitHub Codespaces prebuilds, see GitHub Codespaces prebuilds.